“Trailoring is essential.”
MIL-STD-810H
We will support your work with our services. Our experience and knowledge have been gained through 15 years of testing and providing training services. We also have over 20 years of experience in product development and systems engineering processes.
This page describes the process and considerations for developing an environmental qualification test plan.

Develop Your Test Plan Early!
MIL-STD-810H is a huge guide for testing military equipment for military platforms. This means the described tests must be tailored to fit into your equipment’s intended functions and for the targeted platform use. For this reason, tailoring is essential for developing a test plan for 810 testing. Therefore, developing a test plan for testing your equipment per MIL-STD-810H may take between 1 to 6 months, easily. We strongly recommend not to wait until the end of the testing cycle to complete your test plan. Rather, the test plan must be developed as early as possible, in the initial stage of the project, before design-level efforts start. There are several reasons why you must complete your test plan early; some of these are:
- The specific tests to perform affect your design. The designers must know the test type, test limits, and durations when selecting the solutions.
- A test plan should be complete and used for presenting it to the customer and stakeholders. Early agreements on the tests help identify your design limits early.
For developing a MIL-STD-810 environmental test plan, the following specific studies must be done:
- Selection of test methods and rationale
- Selection of procedures and test type
- Equipment to use
- Identifying the test limits and durations
- detailedDeveloping a detail test procedures and associated forms
We study the Operational Requirements and Life Cycle Environmental Profile for your equipment and develop test requirements. If a Concepts of Operations (CONOPS) document does not exist, we develop one or use the available information to develop an operational requirements document. With this study, the tests selected, methods, procedures, and envelopes to use become specific for testing your equipment. Unlike other test plans, developing a test plan for MIL-STD-810 may take between 1 month and 6 months.
What is Needed?
For your military equipment, we develop test requirements, environmental test plans and test reports, with a research and study with the followin order:
We first develop TEST REQUIREMENTS by identifying the following
- equipment characteristics, functions, modes, and other specfics
- platform requirements
- applicable equipment specs
- equipment’s installation zone in the platform
- relevant rules and regulations
- relevant test standards
- other applicable standards
- test tailoring considerations: Environmental and Mission Profiles)
And develop TEST REQUIREMENTS.
- Please note that the test requirements may include tests from other standards. For example Fire Flammability testing may be a requirement for your equipment and that is not included in MIL-STD-810.
- Test requirements are list of the requirement statements and rationale.
Then, we develop the Test Plan accordingly. When the test plan is complete, the test budget can be recommended.
Contents of an Environmental Qualification Test Plan

Systems engineering personnel appointed to develop a test plan must include the considerations explained in the paragraphs above. A test plan should be formatted such that it should generally include the following areas:
- Purpose statement.
- An introduction providing scope and background.
- A description of the test article, its components, and how it operates.
- A description of test requirements, including information for any deviation from this
document due to the applicability of the requirements. - Test setup, functional performance procedures, support equipment and facilities to be used.
- Specific safety concerns that the test article may pose during the tests along with risk
mitigation plans in accordance with (IAW) organizational safety policies and procedures. - Any planned on-ground or in-flight form, fit, and function checks.
- Performance or physical susceptibility criteria.
- List of reports to be generated.
- A test schedule.
- Referenced documents.
Phases of a Test Project
Understanding the phases of a test and evaluation project helps organize and plan better. The project phases should be included in a separate section, which may be called “Test Process and Phases.” For example, a test project may be divided into the following sections:
- Baseline/Performance Assessment: If this step is performed with a team of experts (Integrated Product Team) and users or user representatives, many potential issues can be solved before starting the physical tests, which can save time, effort, and money. The baseline assessment also helps the personnel familiarize themselves with the equipment and prepare a test plan and test formfor use in each test.
- Verification of the key performance parameters to measure with tolerances
- Verify the operational configuration of the item in its actual platform and define this configuration with limitations.
- Develop required fixtures before the tests. The configuration must represent the components and the platform configuration with geometry, parts, components, material types, etc.
- Quick evaluations of the equipment given test methods, i.e., acceleration, vibration, contamination by fluids, temperature, solar radiation, etc. In many projects, we have identified issues that would happen during the tests.
- Human interface items, if there are any. Those items must be assessed, i.e., in accordance with MIL-STD-1472 Human Factor Assessment
- Review the design and ensure that additional test standards are included due to the equipment’s design specifics, i.e., equipment with textile should be evaluated with other mil specs (type “textile” in Assist quick search tool). Although it is a colossal test standard/guide, MIL-STD-810H does not include many tests that may be required based on the equipment’s specific mission and its design specifics. Another example is that equipment must be tested for fire flammability, which is not included in MIL-STD-810H. These examples can be increased to being too many!
- Test Plan Document Development. Develop the test plan with all considerations explained throughout this article. Developing a test plan for an 810 project may take up to six months if all information is not available!
- Test Phase: The test plan should include the test method, standards to use, a summary of specific procedures tailored to its mission and Life Cycle Environmental Profile (LCEP), test criteria for each test method, test locations, and approximate test schedule. All lab tests are considered as verification tests as per the systems engineering processes.
- Validation Tests: Any ground or flight, road, or seakeeping tests implemented with the user’s involvement in the actual operational environment.
- Reporting: Test results must be evaluated for risks and limitations. A risk assessment may be accommodated for any unexpected test results using MIL-STD-882. The test report must include.
Our Expertise
Our team has experienced test managers, Certified Verification Engineers (CVEs), and subject matter experts. If not, we will propose the appropriate team and fully manage the project. In our team, Dr. Ismail Cicek worked in several test locations in the USA and Turkey and is still managing a test facility called the Marine Equipment Test Center (METC) in Tuzla, Istanbul. He has completed over fifty test projects in the USA test labs where he worked and is now more in numbers at METC and the METC personnel.
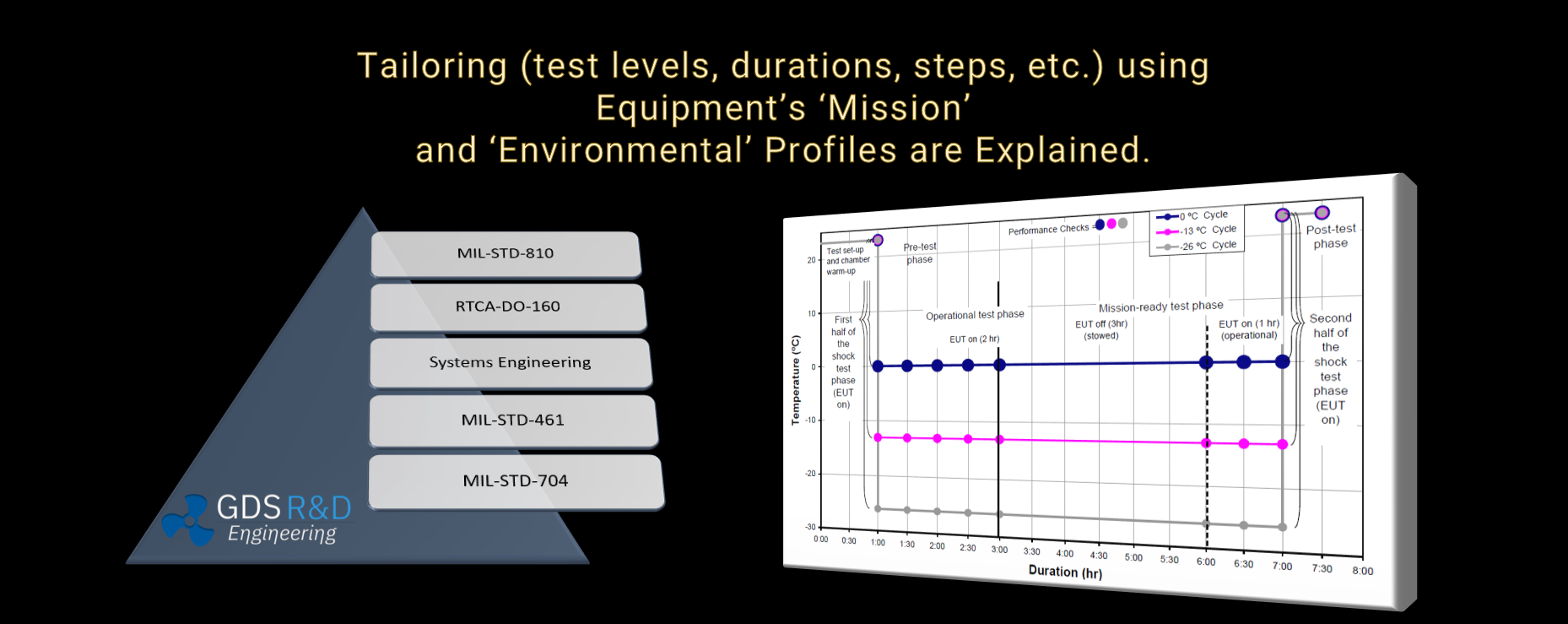
MIL-STD-810H: Tailoring is Essential!
MIL-STD-810H, US DOD Test Standard, starts with an important phrase at the beginning paragraph of each of the 28 test methods: “Tailoring is Essential.” It is therefore crucial to understand what this means and how to tailor the test methods for specific equipment, considering the platform, mission, and environmental requirements.
GDS Engineering R&D provides MIL-STD-810H training online or onsite. Performing operations in various parts of the world, we have been providing this course to the defence industry strategists, leaders, program managers, projects managers, designers, and test engineers for more than 10 years. With long years of background in test projects in the USA and Turkey, Dr. Cicek, the main lecturer of this training, explains the tailoring concepts with specific examples.
This course provides with information and knowledge of experience on how to develop Concepts of Operations (CONOPS) document and Lice Cycle Environmental Profile (LCEP) to derive operational therefore test requirements for the Equipment Under Test (EUT). Understading the tailoring part of MIL-STD-810H is probably the most important aspect of this test standard training, due to the following reasons:
- Developing a test plan for MIL-STD-810H equipment testing might be a confusing and time consuming process.
- Training will provide an understanding into why and when CONOPS document is needed and how test requirements are established along with Mission and Environmental profiles of the EUT. These are all covered by both presentations and specific product examples through discussions during the training sessions.
- In test method discussions, the instructor discuss “what items” (i.e. test levels) and “how” they will be tailored with specific examples.
Test methods, i.e., temperature, humidity, and temperature shock, require mission and environmental profiles to be established for successfully determining the test levels, durations, and criteria for pass or fail.
What to do for Tailoring?
A Generalized Task Statement for Tailoring: Condider the environmental effects. An example list is provided with a list below. Develop exposure curves considering exposure scenarios. For this, use/develop CONOPS document and generate a Life Cycle Environmental Profile (LCEP).
- The equipment is in different operational modes: transportation, operation, and stand-by. Consider these effects with scenarios. Environmental effects (temperature, humidity, icing, etc.) on the equipment in different operational modes, i.e., transportation, operation, and stand-by. Consider these effects with scenarios and develop exposure curves.
- Equipment vulnerabilities under environmental/operational conditions.
- Effects caused by the platform operations (vibrations, shock, etc.)
- The effect due to the platform environment; various conditions in the section the equipment will be operating. For example, the equipment might be exposed to fluid contamination in the section where it will be installed.
- Equipment’s effect to the environment and systems (EMI, vibrations, fluid contamination, fire and flammability, etc.)
- Consider risks of operational breakdowns with “what if” scenarios
How does Life Cycle Environmental Profile (LCEP) affect the test procedures?
- LCEP should be developed for selecting the levels and durations of the environmental tests, especially the ones include climatic data.
- Each operational modes (transportation, operational, storage, stand-by, etc.) should be considered.
- Equipment that is diretly exposed to the external environment should consider the meteorological data, provided in MIL-STD-810H Part I and Part III as well as MIL-STD-310 and AECTPs.
- Equipment that is not directly exposed to external environment should consider internal conditions, considering the maximum levels and duration of exposure.
How does Mission Profile affect the test procedures?
- Equipment’s modes and the durations to exposures could only be identified with clearly specifying the mission profile for the equipment.
Your equipment, for example, could be a device that must demonstrate fire resistance. In that case, it is important to understand the aircraft fire zones and applicable procedures. For this, we review the test standard and FAA/EASA documents to fully understand the described requirements and specs and develop a test case and procedure.
Risk analysis is another consideration.
- The results are not always pass or fail. We perform risk analysis to demonstrate, and if the result is negligible, we recommend alternate methods to pass. For items that do not pass the tests, we recommend design changes based on similar equipment tests or results.
Additional Links for More Reading:
Tailoring is Essential: Our dedicated page describes more about tailoring.
Training on MIL-STD-810H Testing: Our online training details are provided. A good training helps your personnel develop better test plans and save time, effort, and money at the project completion.
Check out our calendar for training programs: GDS Training Calendar.
Systems Engineering training courses provided by GDS Engineering R&D (including MIL-STD-810H, RTCA-DO-160G, MIL-STD-461G, Requirements Management, MIL-STD-704F, and EMI/EMC General Training: Information is provided on this page.