The increase in shipping activity globally has resulted in an increased awareness of impacts on the marine environment. Effects of noise pollution, especially on marine life, have become highly prominent. Marine life is extremely sensitive to noise pollution. Due to their extreme reliance on underwater sounds for basic life functions like searching for food and mate and an absence of any mechanism to safeguard them against it, underwater noise pollution disrupts marine life (Singla, 2020). In short, marine animals depend on sound to live, making and listening to it in various ways to perform various life functions (US Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, 2014).
Noise travels much more in water, covering greater distances than it would do on land while travelling through air. Underwater sound has both pressure and particle motion components and hearing can be defined as the relative contribution of each of these sound components to auditory detection (Popper AN, 2011). Sounds radiated from ships are among the underwater noise sources. Among shipborne Underwater Radiated Noise (URN) sources are the following:
- Propeller’s rotational turn and the blades hitting to water flow lines
- Propeller’s cavitation
- Ship hull structure’s interaction water (fluid-structure interaction)
- Mechanical noises from onboard machinery
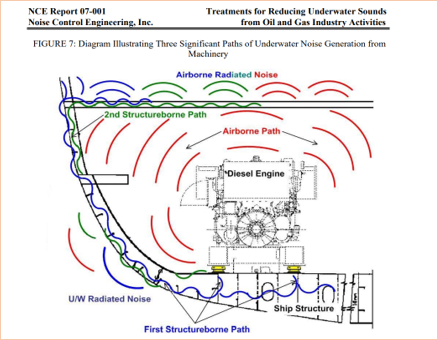
Click here to read the report generated by NCE (NCE Report 07-001, 2007)
All of these noise sources are radiated to underwater from ships, especially when the ship speed is at higher rates, i.e. above 15 knots.
When a Powership is considered, out of the 4 aforementioned noises, only mechanical noise sources are of concern as there are no noises that emanate from the other three sources because the Powership is docked. Mechanical onboard noises are still of concern and therefore need to be evaluated and tested for the assessment of their potential negative effects to marine life.
GDS Engineering R&D has the capability for measuring the underwater radiated noise and assessment of the results based on the effect to the sealife in the region.
