The Importance of EMI Shielding in Enclosure Design for EMI/EMC Compliance
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding is critical in enclosure design to ensure compliance with rigorous standards like RTCA-DO-160G and MIL-STD-461G. These standards govern the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of electronic equipment in aviation and military applications, respectively, and require devices to perform reliably in environments with high EMI levels.
Enclosures serve as the first line of defense against EMI, preventing unwanted electromagnetic energy from penetrating or escaping. Proper shielding ensures that internal components are protected from external interference, such as radio frequencies, and prevents emissions from interfering with surrounding equipment. Without effective shielding, devices are likely to fail compliance tests, leading to costly redesigns and delays in product development.
Incorporating EMI shielding materials, such as conductive paints, metal coatings, or gasketed seams, is essential. These materials block or redirect electromagnetic waves, reducing the risk of signal degradation and component malfunction. Key considerations include the material’s conductivity, thickness, and proper sealing of openings like vents and access panels.
Successful compliance with RTCA-DO-160G and MIL-STD-461G not only ensures product reliability but also enhances safety and operational efficiency in demanding environments. A well-designed shielded enclosure is vital for meeting these standards and achieving optimal device performance in aviation and military contexts.
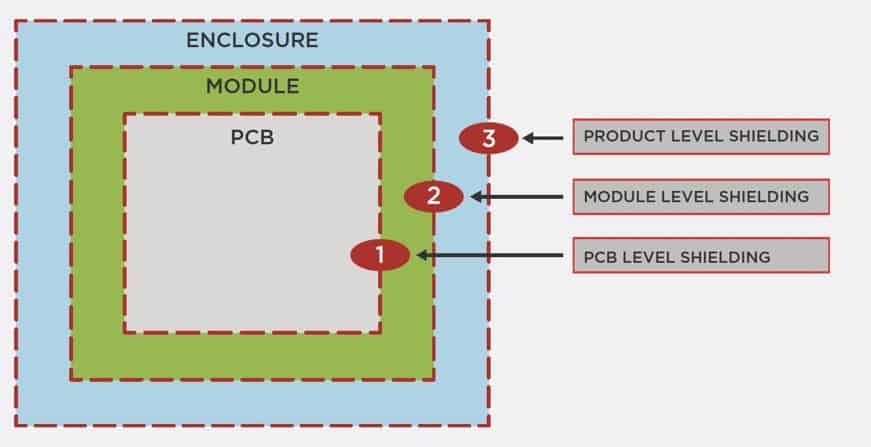
Solutions for EMI Shielding in Enclosure Design for EMI/EMC Compliance
To ensure EMI/EMC compliance, effective shielding solutions must be integrated into enclosure design. Here are the key solutions:
1. Conductive Coatings and Paints
- These are applied to non-metallic surfaces, such as plastic enclosures, to create a conductive layer that blocks electromagnetic waves. Common materials include silver, copper, and nickel-based coatings.
2. Metallic Enclosures
- Using metals like aluminum or stainless steel for the enclosure itself provides natural shielding. These materials effectively reflect and absorb electromagnetic interference.
3. EMI Gaskets and Seals
- Conductive gaskets made from materials like metal mesh or conductive elastomers seal joints and openings to prevent gaps where EMI could penetrate or escape.
4. Shielded Vents and Filters
- For enclosures requiring airflow, shielded vents with honeycomb or mesh designs allow air to pass while blocking EMI. Filters on cable penetrations further enhance shielding.
5. Seam Design and Fastening
- Overlapping seams, tight tolerances, and conductive fasteners minimize leakage points. Proper grounding ensures continuous conductivity throughout the enclosure.
6. Cable Shielding and Grounding
- Shielded cables and proper grounding techniques reduce emissions and susceptibility to external interference.
7. Internal Component Shielding
- For sensitive components, internal shielding solutions like metal cans or conductive tapes provide localized protection.
Combining these solutions in enclosure design ensures compliance with standards like RTCA-DO-160G and MIL-STD-461G, guaranteeing reliable performance in high-EMI environments.
A General Information on the EMI/EMC Shielding Paints
EMI/EMC shielding paints are specialized coatings that provide a barrier against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). They are crucial in various industries, including electronics, aerospace, telecommunications, and automotive, where sensitive electronic components need protection from electromagnetic radiation.
These paints work by incorporating conductive fillers, such as silver, copper, nickel, or carbon, into a binder matrix. The conductive fillers create a pathway for electromagnetic energy to be reflected or absorbed, preventing it from disrupting the operation of electronic devices.
Key Properties and Benefits:
- Conductivity: Provides effective attenuation of electromagnetic waves.
- Shielding Effectiveness: Measured in decibels (dB), indicating the amount of EMI reduction.
- Corrosion Resistance: Protects against environmental factors.
- Adhesion: Ensures good bonding to various substrates.
- Flexibility: Allows for application on complex shapes.
- Application Methods: Can be applied by spraying, brushing, or dipping.
Applications:
- Electronics Enclosures: Shields electronic devices from external EMI.
- Aerospace and Defense: Protects sensitive avionics and communication systems.
- Medical Devices: Ensures EMC for patient safety.
- Automotive: Shields electronic components in vehicles.
- Telecommunications: Protects communication equipment from interference.
Choosing the right EMI/EMC shielding paint depends on factors like:
- Shielding effectiveness required
- Frequency range of interference
- Operating environment
- Substrate material
- Application method
By effectively mitigating EMI, these paints ensure the reliable operation of electronic devices and systems, prevent data loss, and maintain signal integrity.
Application Examples

Here is some application several examples for EMI EMC shielding:
1. Shielding Enclosures for Electronic Devices
- Problem: Electronic devices like laptops, smartphones, and routers emit electromagnetic radiation that can interfere with other devices or be susceptible to external interference.
- Solution: EMI/EMC shielding paints are applied to the inside of plastic enclosures housing these devices. This creates a conductive barrier that blocks radiation, ensuring proper functioning and preventing data corruption.
2. Aerospace Applications
- Problem: Aircraft avionics and communication systems are highly sensitive to EMI, which can compromise flight safety.
- Solution: Shielding paints are used on aircraft panels, cockpit instruments, and communication equipment to protect them from interference caused by lightning strikes, radar signals, and other electromagnetic sources.
3. Medical Devices
- Problem: Medical devices like pacemakers, defibrillators, and MRI machines need to operate without interference to ensure patient safety.
- Solution: EMI/EMC shielding paints are applied to the casings of these devices to prevent electromagnetic radiation from affecting their performance or causing malfunctions.
4. Automotive Industry
- Problem: Modern vehicles are packed with electronic systems that can interfere with each other or be affected by external EMI.
- Solution: Shielding paints are used on various components, including engine control units, entertainment systems, and sensors, to prevent electromagnetic interference and ensure reliable operation.
5. Telecommunications Infrastructure
- Problem: Cell towers, antennas, and other telecommunications equipment are susceptible to interference from various sources.
- Solution: Shielding paints are applied to these structures to minimize interference and maintain signal quality.
6. Secure Facilities
- Problem: Sensitive data centers, government buildings, and military installations need protection from electromagnetic espionage and data breaches.
- Solution: EMI/EMC shielding paints are applied to walls, ceilings, and floors to create a secure environment that blocks electromagnetic signals from entering or leaving the facility.
7. EMI Shielding Gaskets
- Problem: Gaps and seams in electronic enclosures can allow electromagnetic radiation to leak in or out.
- Solution: Conductive paints can be used to create EMI gaskets that fill these gaps, providing a continuous conductive seal.
These are just a few examples of how EMI/EMC shielding paints are used across various industries to protect sensitive electronics and ensure electromagnetic compatibility. As technology advances and electronic devices become more prevalent, the importance of these specialized coatings will only continue to grow.
MIL-STD-461G EMI-EMC Training
We provide training on the MIL-STD-461G EMI/EMC testing and we include the design tips such as found on this web page. We include all design tips including electrical design in our training.
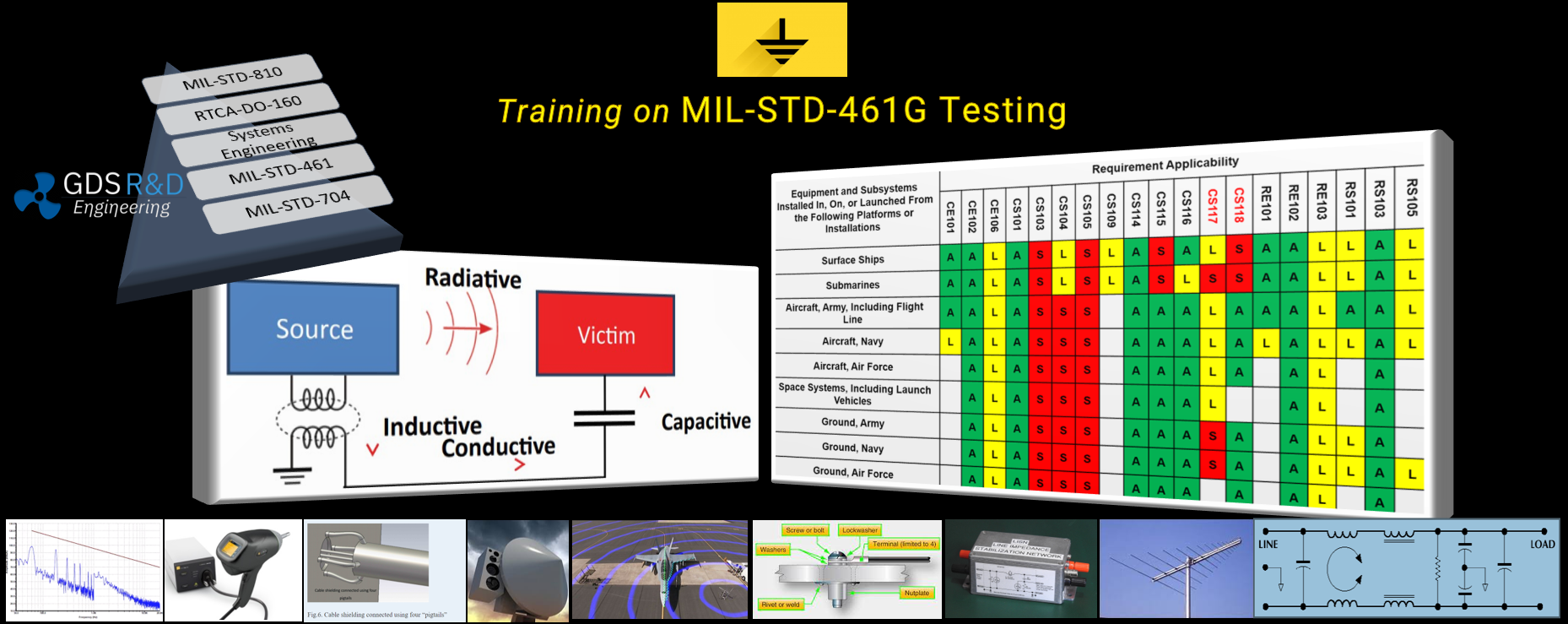
RTCA-DO-160G Training
We provide training on the RTCA-DO-160G testing and we include the design tips such as found on this web page. We include all design tips including electrical design in our training for a better EMI shielding, especially for enclosures.


