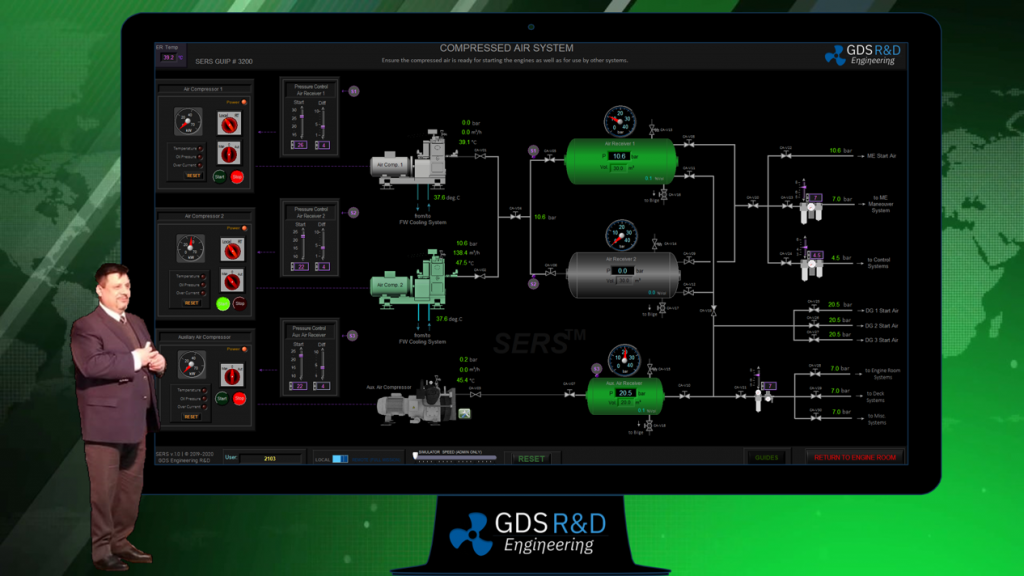
Description of an ERM Training
Engine Room Resource Management (ERM) is a system of achieving safe engineering operations by proactively utilizing and managing personnel, equipment, and information in the machinery space. A review the team roles, human factors, and situational awareness is required to plan and implement a proper ERM program. Remember, good ERM practices can save personnel and vessels from unwanted risks.
The course complies with the standards of Regulation III/1, III/2, III/6 and VIII/2 of STCW Convention, Section A-III/1, III/2, III/6, A-VIII/2 and B-VIII/2 of STCW Code and SIRE requirements.
Topics in a ERM training includes
- Learn about effective resource allocation including crew, plant, equipment, and information management
- Understand the leadership responsibilities of the Chief Engineer, including staff training and motivation, preventing crew fatigue, and conducting appropriate drills
- Review individual and team roles, and how to reduce human error using situational awareness and closed loop communication
- See engine room equipment functions and standard operating procedures
Relevance of this Training with existing IMO Model Courses
This course includes the topics using the guidance provided by the following IMO Model Courses.
- IMO Model Course 7.02 Chief Engineer Officer and Second Engineer Officer
- IMO Model Course 7.04 Officer in Charge of an Engineering Watch
- IMO Model Course 2.07 Engine Rooms Simulator. 2017 Ed.
- IMO Model Course 1.39 Leadership and Teamwork
- IMO Model Course 1.38 Marine Environmental Awareness
Referenced Documents
The following documents must be used along with this document for effectively planning and providing an ERM training.
GDS SERS User Manuals and Documents
- User Manual Vol I (SERS Software Description) describe the SERS software with the SERS Graphical User Interface (GUI) Panels accessed from the SERS Main Graphical User Interface (GUI) Panel.
- User Manual Volume II (Engine Room Operations) includes the operational instructions on how to operate the engine room systems and machinery using the SERS.
- User Manual Vol III (Installation & Configuration) describes the installation and the configuration of software and hardware items
- This manual, User Manual Volume IV (Instructor’s Manual), includes guides and information for the instructors to utilize SERS in their trainings according to their specific training objectives.
- Refer to “SERS Philosophy Document” for selecting the configuration of the SERS for your training objectives. Then use Vol. III for the proper installation of the SERS and reading the configuration guidelines.
External Referenced Documens
- IMO Model Course 7.02 Chief Engineer Officer and Second Engineer Officer
- IMO Model Course 7.04 Officer in Charge of an Engineering Watch
- IMO Model Course 2.07 Engine Rooms Simulator. 2017 Ed.
- IMO Model Course 1.39 Leadership and Teamwork
- IMO Model Course 1.38 Marine Environmental Awareness
ENGINE ROOM RESOURCE MANAGEMENT TRAINING MODEL
Engine Room Resource Management (ERM) is a system of achieving safe engineering operations by proactively utilizing and managing personnel, equipment, and information in the machinery space. A review the team roles, human factors, and situational awareness is required to plan and implement a proper ERM program. Remember, good ERM practices can save personnel and vessels from unwanted risks.
The course complies with the standards of Regulation III/1, III/2, III/6 and VIII/2 of STCW Convention, Section A-III/1, III/2, III/6, A-VIII/2 and B-VIII/2 of STCW Code and SIRE requirements.
The course is aimed at officers of the engineering watch (operational level), 2nd Engineer and Chief Engineer (management level).
The course is a mix of theory case studies and simulation exercise covering topics below. The following are the four main areas to cover in an ERM training:

- RESOURCE ALLOCATION: Effective resource allocation including crew, plant, equipment, and information management.
- LEADERSHIP: The leadership responsibilities of the Chief Engineer, including staff training and motivation, preventing crew fatigue, and conducting appropriate drills
- TEAM ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES: The roles and responsibilities for both individuals and team. Planning and execution must be reviewed with past experiences with the aim of reducing human error using situational awareness and closed loop communication.
- TECHNICAL OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT: A study with a thorough review of equipment functions, standard operating procedures including safety procedures.
Designing your ERM Training with SERS
In this section, we provide a guidance on how to design an IMO ERM training with step by step approach. We hope that it helps you provide an effective training for your cadets or engineers already working onboard.
1. Certification of the Simulator
Certification of the simulator is highly important. You must ensure that it has all capabilities to provide the capabilities training based on STCW 2010. As for the ERM training, the simulator must be capable of demonstrating the IMO Model Course (2.07) exercises.
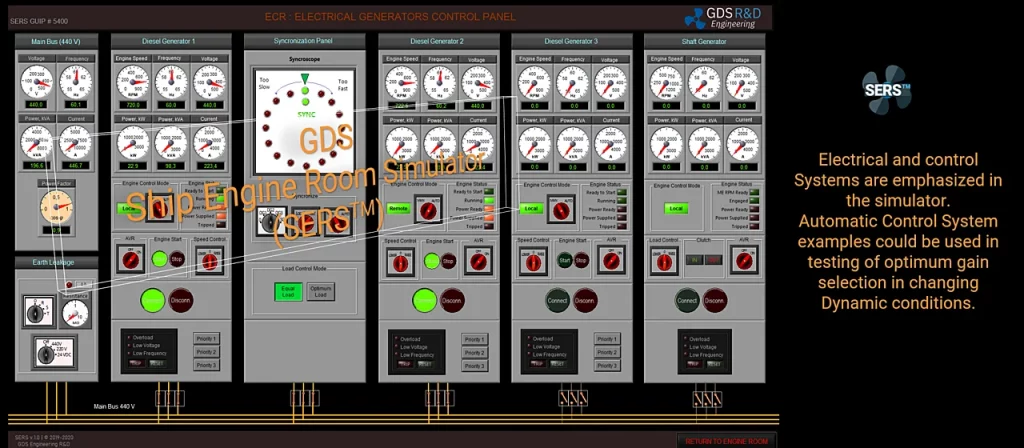
GDS Ship Engine Room Simulator (SERS™) is a Training Simulator System with a Full Mission (Class A) type approval certificate obtained from ClassNK. ClassNK is an IACS affiliate Classification Organization. Certificate of SERS™ lists the IMO STCW 2010 competencies, as provided in Table 1, which includes the compliance to IMO STCW Tables A-III. The class certification of SERS includes the IMO Model Course 2.07 (207) Ed.). The trainee is able to perform all exercises contained in the IMO Model Course 2.07. All exercises were demonstrated during the Class Type Approval.
Table 1: SERS™ Certification Items for STCW Training Competencies.
| IMO STCW-2010 Reference | Competence |
| Table A-III/1.1 | Maintain a safe engineering watch |
| Table A-III/1.2 | Use English in written and oral form |
| Table A-III/1.3 | Use internal communication systems |
| Table A-III/1.4 | Operate main and auxiliary machinery and associated control systems |
| Table A-III/1.5 | Operate fuel, lubrication, ballast and other pumping systems and associated control systems |
| Table A-III/1.6 | Operate electrical, electronic and control systems |
| Table A-III/1.10 | Ensure compliance with pollution prevention requirements |
| Table A-III/1.11 | Maintain seaworthiness of the ship |
| Table A-III/1.12 | Prevent, control and fight fires on board |
| Table A-III/1.16 | Application of leadership and team working skills |
| Table A-III/2.1 | Manage the operation of propulsion plant machinery |
| Table A-III/2.2 | Plan and schedule operations |
| Table A-III/2.3 | Operation, surveillance, performance assessment and maintaining safety of propulsion plant and auxiliary Machinery |
| Table A-III/2.4 | Manage fuel, lubrication and ballast operations |
| Table A-III/2.5 | Manage operation of electrical and electronic control equipment |
| Table A-III/2.6 | Manage troubleshooting restoration of electrical and electronic control equipment to operating condition |
| Table A-III/2.8 | Detect and identify the cause of machinery malfunctions and correct faults |
| Table A-III/2.10 | Control trim, stability and stress |
| Table A-III/2.11 | Monitor and control compliance with legislative requirements and measures to ensure safety of life at sea and protection of the marine environment |
| Table A-III/2.14 | Use leadership and managerial skills |
| Table A-III/4.2 | For keeping a boiler watch: Maintain the correct water levels and steam pressures |
| Table A-III/6.1 | Monitor the operation of electrical, electronic and control systems |
| Table A-III/6.2 | Monitor the operation of automatic control systems of propulsion and auxiliary machinery |
| Table A-III/6.3 | Operate generators and distribution systems |
| Table A-III/6.4 | Operate and maintain power systems in excess of 1,000 volts |
| Table A-III/6.5 | Operate computers and computer networks on ships |
| Table A-III/6.7 | Use internal communication systems |
| Table A-III/6.9 | Maintenance and repair of automation and control systems of main propulsion and auxiliary machinery |
| Table A-III/6.12 | Ensure compliance with pollution-prevention requirements |
2. Simulator Detail Specs
This is probably the most tricky part. Some simulators could be cheap (!) and may be simulating the systems at a very high level. Does it have a main engine lubricating oil system? Probably yes. Does it satisfy the IMO competencies. Well this is the tricky part. It must have the LO Temperature Control System appropariately and realistically simulating the systems. We gave a simple example. Most trainers learn the specifics of the simulator after some experience of using it and become aware of the isues that prevent providing an efficient engine room simulator training. This may not be of an issue for a freshman level students; however, it becomes important when trainees are already completed their training onboard a ship and that they completed their marine engine engineering courses (Diesel Engines, Ship Auxiliary Engines, Electrical Systems, Automatic Control Systems, etc.). Additionally, the models and simulated systems has critical importance when the trainees are the personnel already have experience onboard a ship. Usually, the trainees in an ERM course will be watchkeeping officers or even chief engineers and they will probably critisize the training if the simulations are not realistic!
We have written the full specifications list for an engine room simulator, generalized with a focus on how it must help the instructors in the training. We went through each section of both the IMO STCW 2010 and IMO Model Course 2.07 and ensure the full list is at hand with the training in focus. Do not hesitate to request a copy if you are establishing an engine room training facility. We will be glad to help as trainers with ERS training experience of more than 20 years.
We should warn you that you must prepare the requirements for purchasing an Engine Room Simulator not the manufacturer.
3. Simulator Configurations
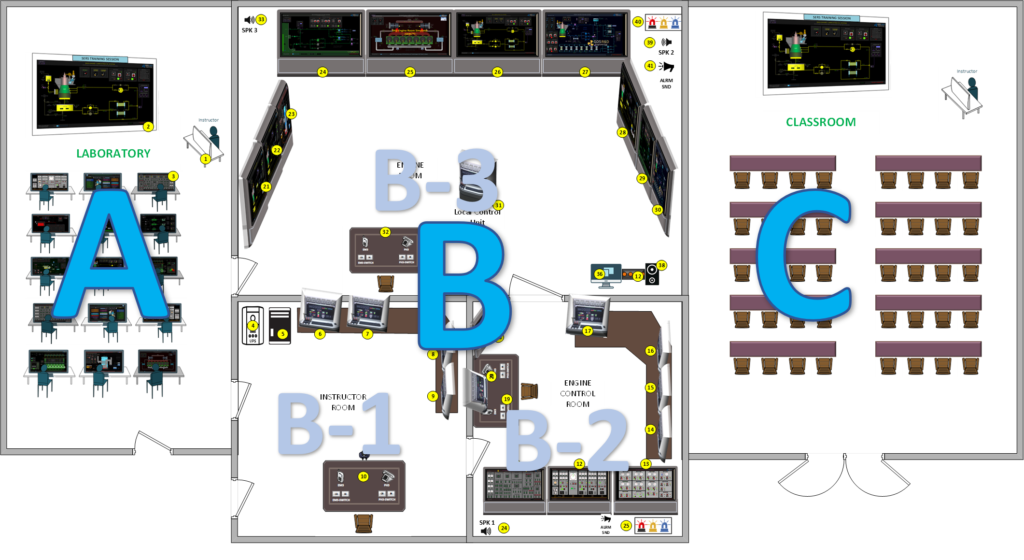
The training area must be organized with a focus into the training goals and objectives. The number of students to train at once is also an important element.
There are two examples of simulator configırations shown with the following figures. You must define your objectives first and ensure that a satisfactory number of stations and area is provided during the training.