Our new paper about SERS™ and ERM Training has been published in the Proceedings of IMLA 29.
Paper Reference Information (APA):
Ismail Cicek and Burak Cavusoglu (2024). An Optimized Ship Engine Room Simulator Configuration for Effective Engine Room Resource Management Training. Proceedings of the International Maritime Lecturers Association (IMLA) Conference. Pages 36-50. Conference held on September 25-28, Istanbul, Turkey.
Download our Paper in PDF File:
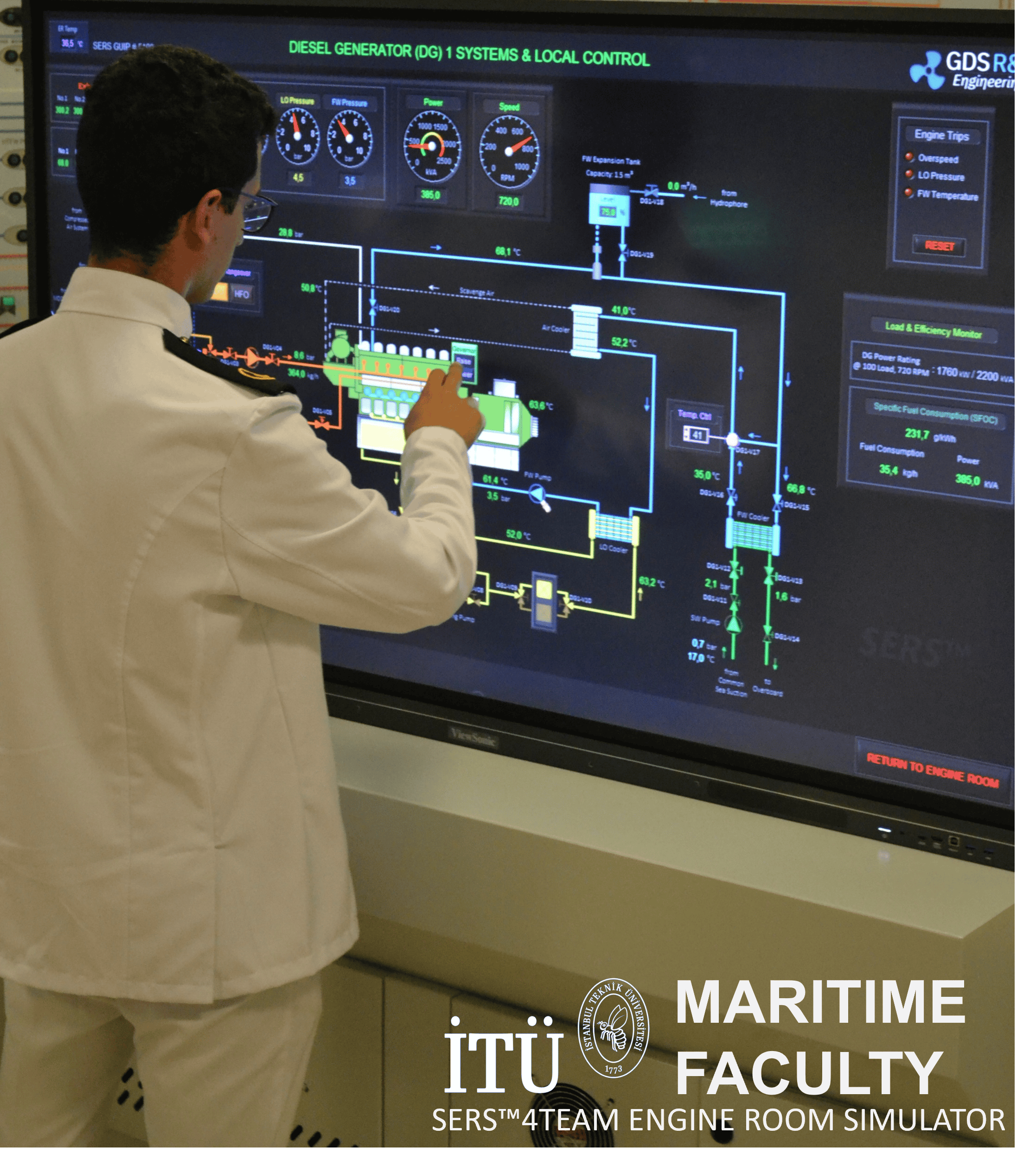
CavusogluCicek-An-Optimize-Shipr-Engine-Room-Simulator-Configuration-for-ERM-trainingAs part of the IMLA 2024 Conference, the new engine room simulator, called Ship Engine Room Simulator (SERS™) 4Team, SERS™4Team, has been demonstrated by Istanbul Technical University.

There was a great interest in the SERS™4Team demonstrations at the GDS booth and demonstrations at the Istanbul Technical University.
Optimizing Maritime Engineering Training: A Deep Dive into the SERS™4Team Simulator
The International Maritime Lecturers’ Association (IMLA) 2024 Conference provided a compelling platform for showcasing advancements in maritime education and training. Among the highlights was the demonstration of Istanbul Technical University’s latest innovation: the Ship Engine Room Simulator (SERS™) 4Team. This cutting-edge simulator offers a significant leap forward in training maritime engineers, addressing critical challenges and aligning with contemporary industry standards.
The SERS™ 4Team distinguishes itself through its robust capabilities for both research and training, focusing on engine performance management within a collaborative teamwork environment. This emphasis on collaborative teamwork is crucial, reflecting the complex and interdependent nature of modern ship engine rooms. The simulator facilitates training in a full mission training configuration, allowing multiple trainees to interact within a virtual engine room environment, mirroring real-world operational dynamics. This approach directly addresses the need for effective communication, coordination, and shared decision-making in critical situations.
A key strength of the SERS™ 4Team lies in its ability to simulate a wide array of scenarios, including those with potentially catastrophic consequences. Notably, the simulator can recreate events leading to a blackout of the ship, a scenario of paramount concern in maritime safety. By allowing trainees to experience and respond to such high-stakes situations in a controlled environment, the SERS™ 4Team fosters crucial decision-making skills and enhances preparedness for real-world emergencies. This focus on critical scenarios directly supports the development of competencies outlined in the IMO STCW 2010 Convention, ensuring that trainees are equipped to handle complex and challenging operational conditions.
Furthermore, the SERS™ 4Team is designed with cost-effectiveness in mind. By providing a virtual training environment, the simulator reduces the reliance on expensive and potentially hazardous onboard training, offering a more sustainable and accessible approach to maritime education. This cost-effectiveness does not compromise the quality of training; on the contrary, the simulator offers a controlled and repeatable learning experience, allowing trainees to practice complex procedures and respond to critical scenarios multiple times, enhancing their understanding and proficiency.
The simulator’s design explicitly incorporates exercises and scenarios derived from the IMO Model Course 2.07, ensuring that training aligns with internationally recognized standards for marine engineering education. This alignment underscores the simulator’s commitment to delivering high-quality, standardized training that meets the evolving demands of the maritime industry. By integrating the principles of Collaborative Teamwork within a Full Mission Training Configuration, and by addressing critical scenarios such as ship blackouts, the SERS™ 4Team offers a powerful tool for optimizing maritime engineering training and enhancing maritime safety, fully supporting the development of IMO STCW 2010 Competencies. This innovative approach to training promises to significantly contribute to the development of competent and resilient maritime engineers.
Download the Full Proceedings: IMLA 2024 Conference Proceedings held between 25-28 September 2025, Istanbul, Turkey:
Proceedings-of-IMLA-29
