In recent years, the maritime industry has seen a significant push towards technological advancement and stricter safety and operational standards. As vessels become more sophisticated and regulations evolve, the role of well-trained onboard maritime personnel becomes increasingly essential. In this context, the SIRE 2.0 program and GDS Ship Engine Room Simulator represent pioneering tools designed to equip maritime crews with deep technical skills necessary to meet new demands and improve the safety and efficiency of maritime operations.
Understanding SIRE 2.0 and Its Impact on Maritime Training
The Ship Inspection Report Programme (SIRE) has long been a fundamental tool in maintaining safety and operational standards across the maritime industry, particularly for tanker operations. Launched by the Oil Companies International Marine Forum (OCIMF), the program provides a comprehensive inspection system that evaluates the condition and operations of vessels. However, with the growing complexity of modern vessels and stricter environmental and safety regulations, the traditional SIRE program required enhancements to address these evolving needs. This led to the development of SIRE 2.0, an upgraded version that integrates data-centric inspection methodologies with a stronger focus on crew competency, operational excellence, and technical skills.
One of the key features of SIRE 2.0 is its focus on assessing the competency of crew members in handling complex equipment and operations. Rather than focusing solely on vessel condition, SIRE 2.0 evaluates the practical skills, knowledge, and decision-making abilities of onboard personnel. This ensures that crew members are not only familiar with equipment and operational standards but are also capable of responding effectively to critical situations.
The emphasis on crew competency in SIRE 2.0 aligns with the industry’s shift toward a human-centered approach in safety and operational excellence. This paradigm shift means that training programs must go beyond traditional instruction and delve into more practical, technology-driven skills, which is where simulators like the GDS Ship Engine Room Simulator come into play.
The Role of the GDS Ship Engine Room Simulator in Skill Development
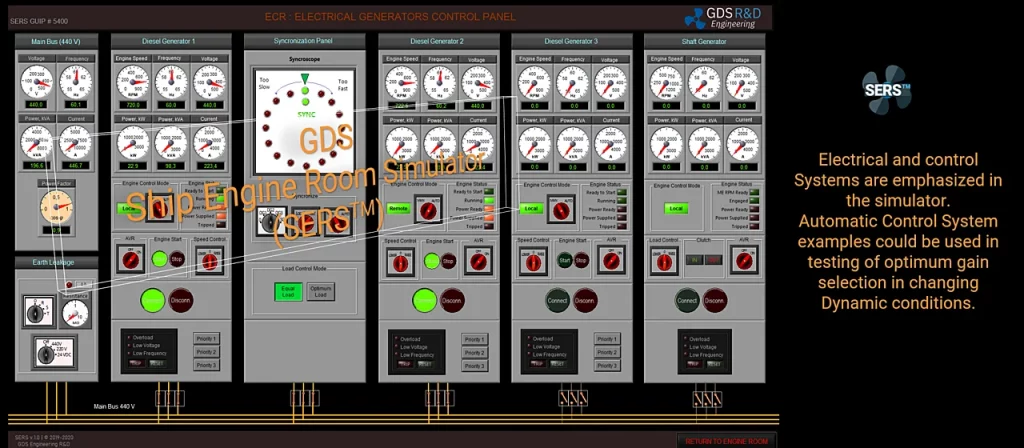
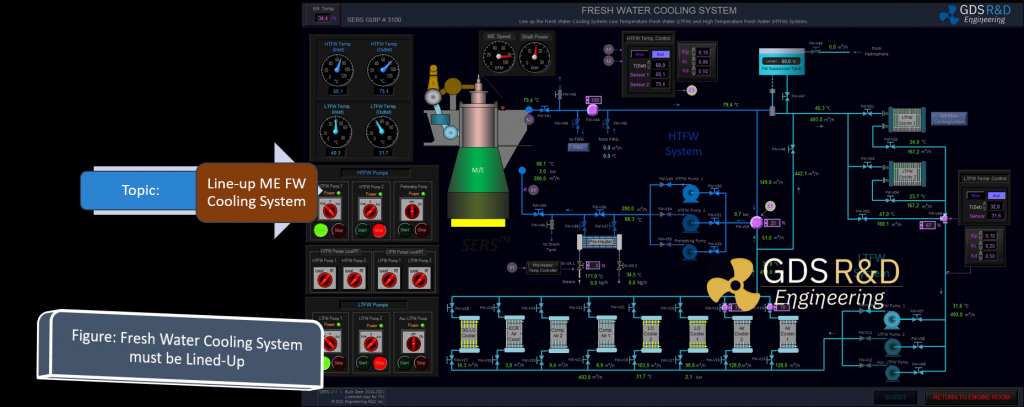
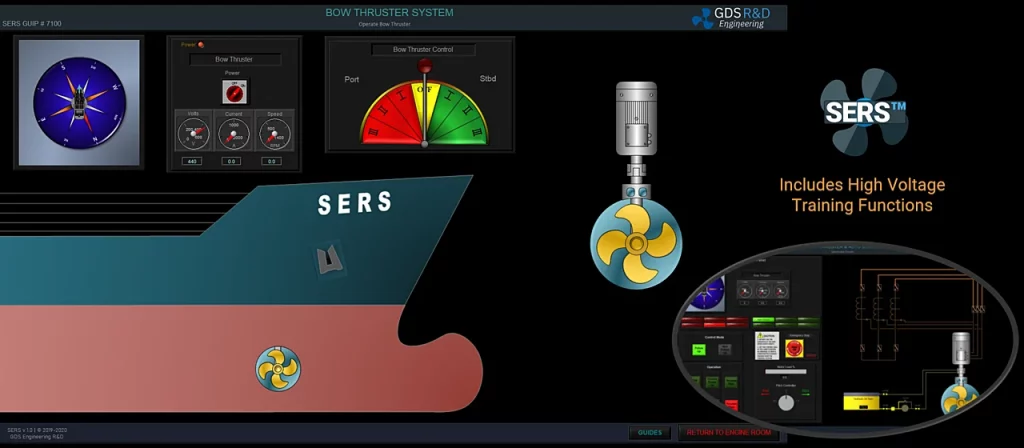
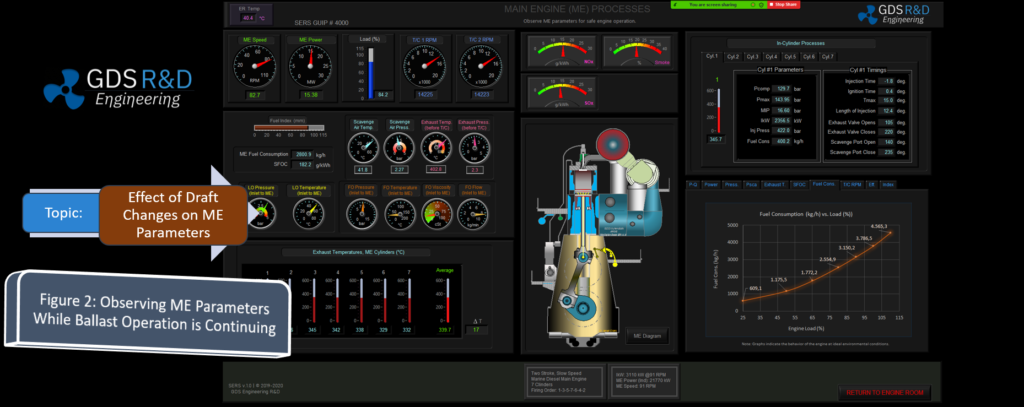
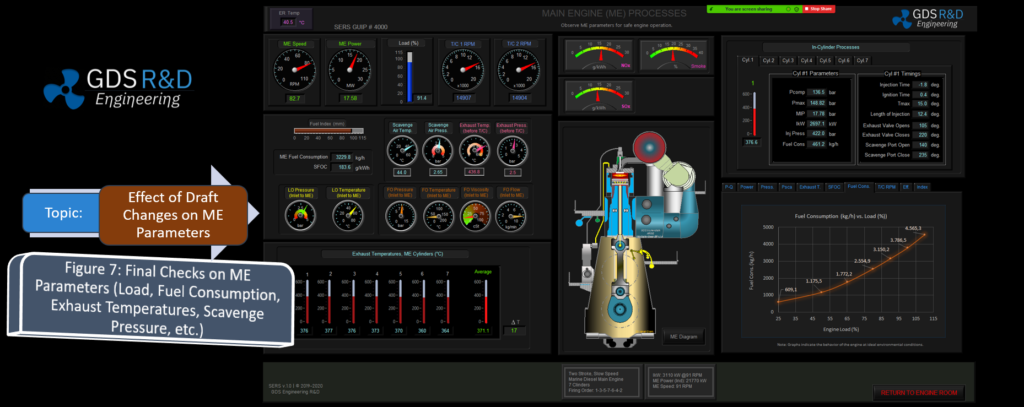
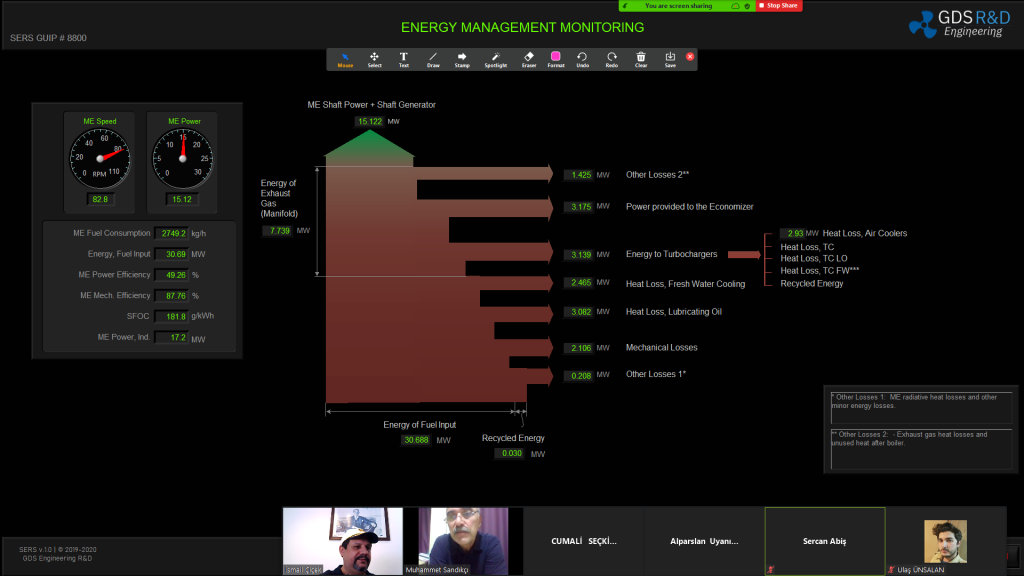
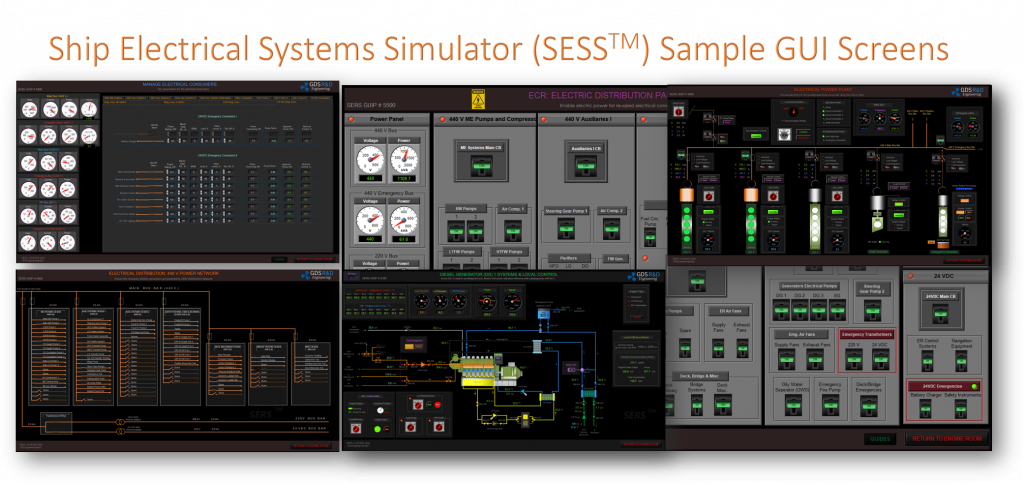
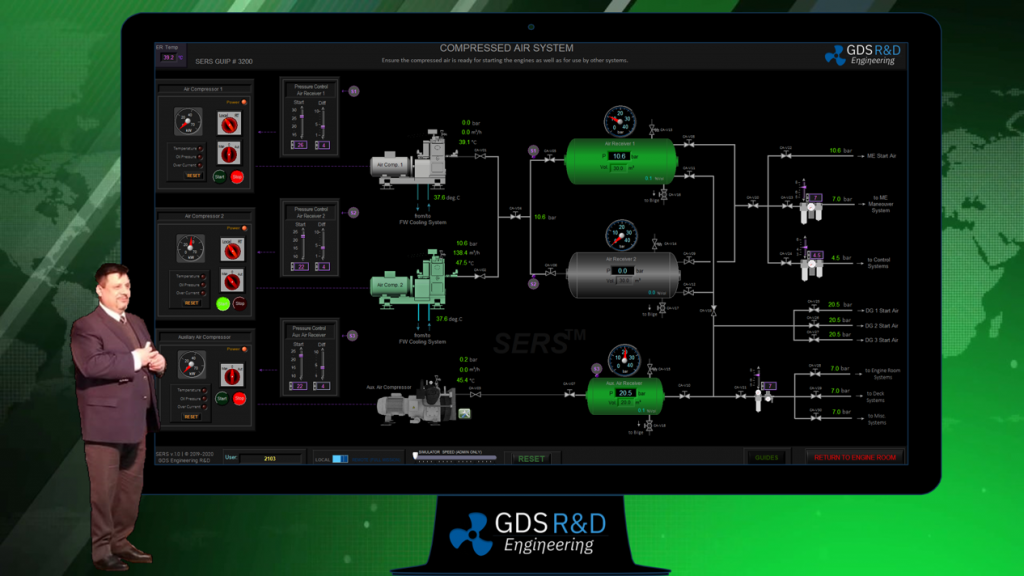
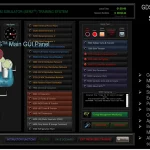
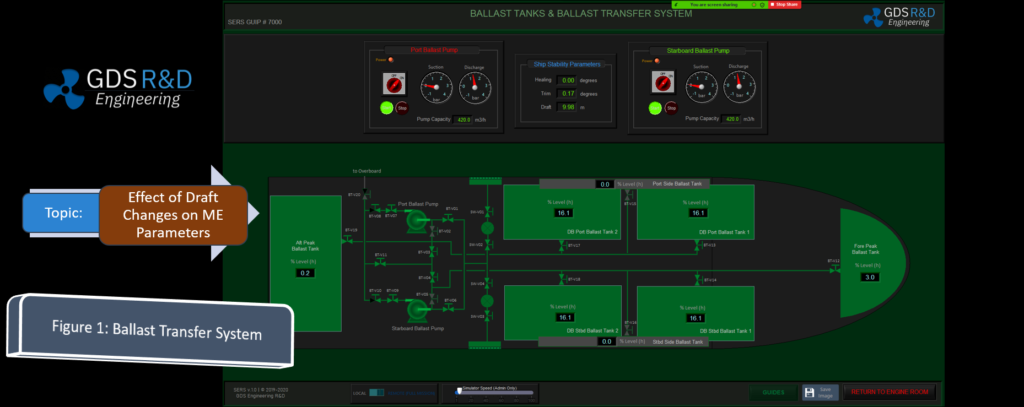
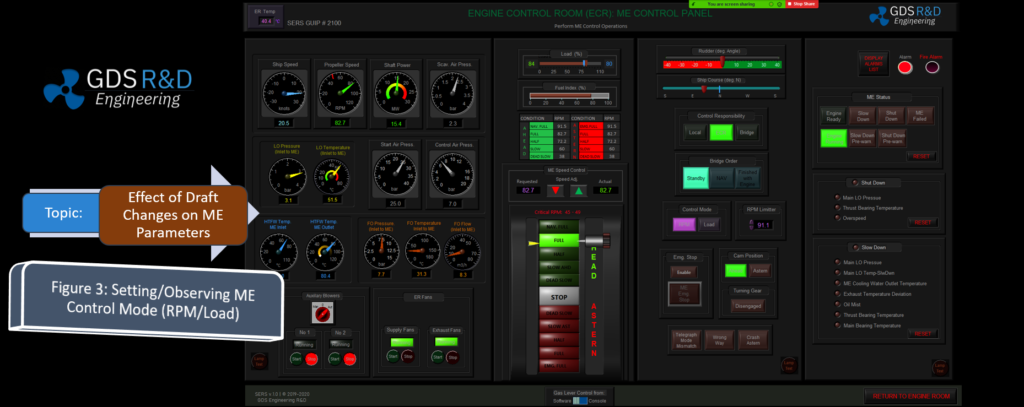
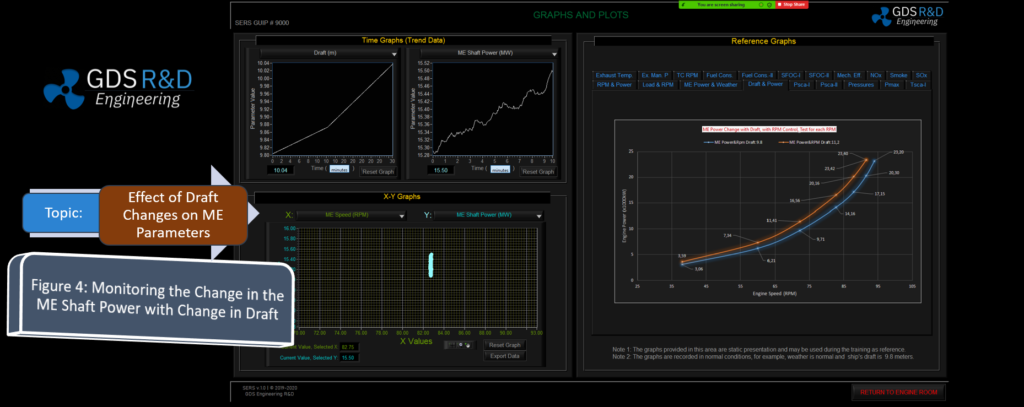
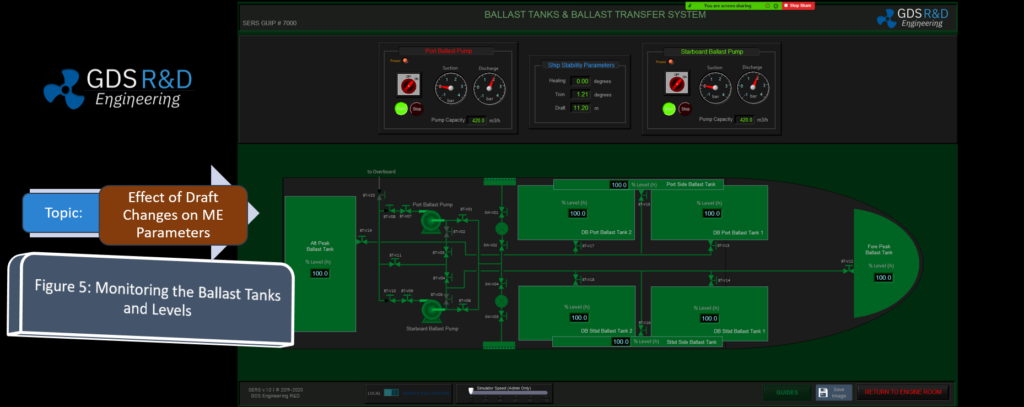
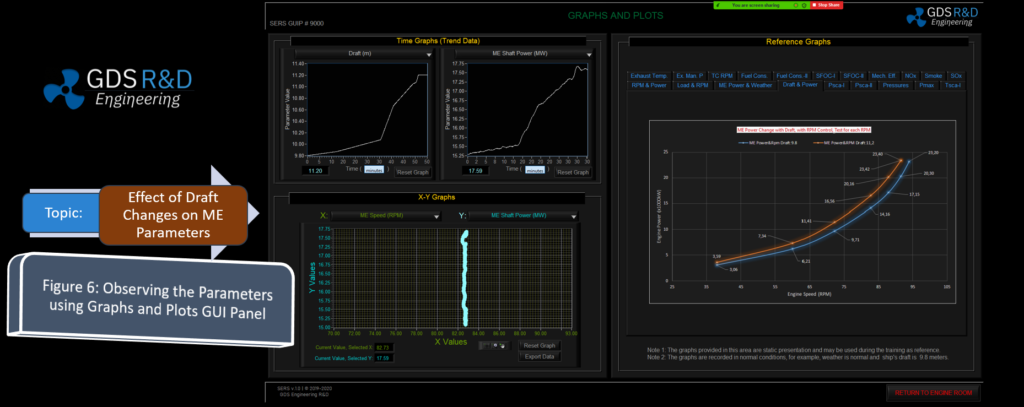
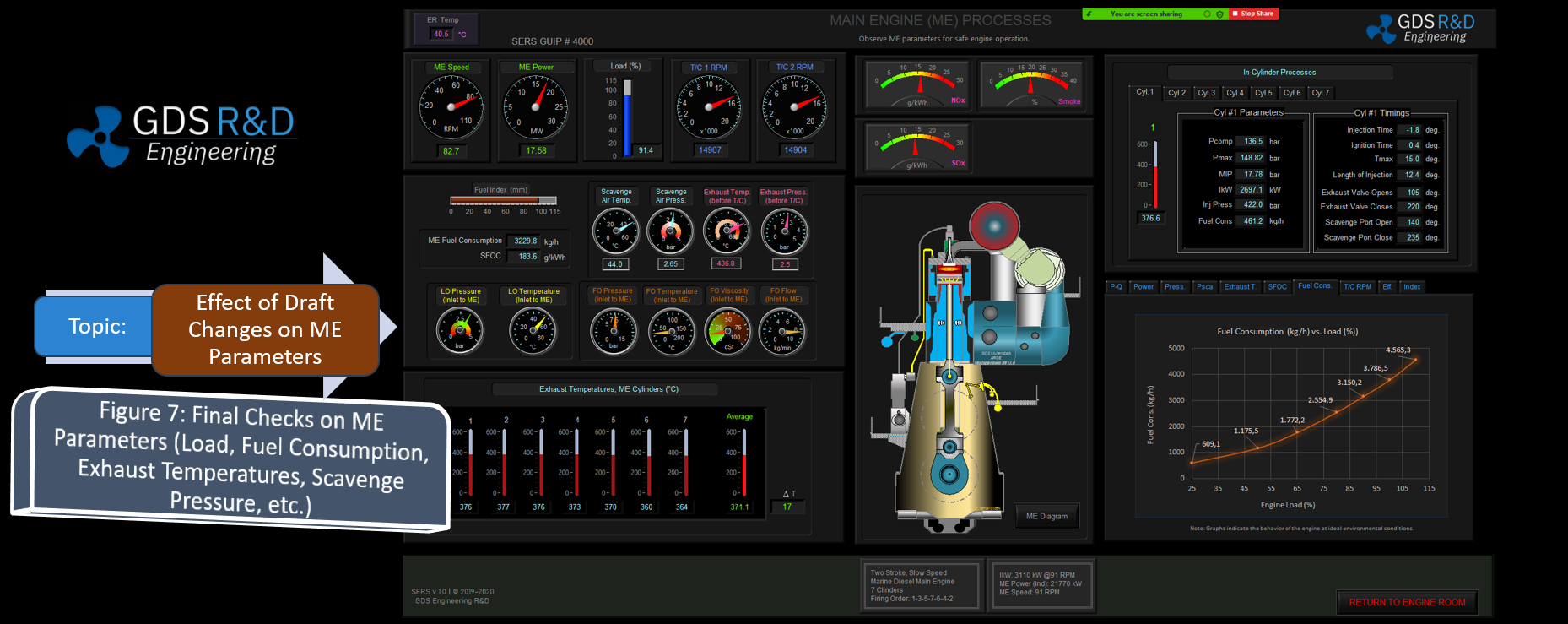
The GDS Ship Engine Room Simulator is an advanced training tool that replicates the engine room environment of modern vessels, providing maritime personnel with hands-on experience in a controlled setting. This simulator covers a wide range of critical systems found in ship engine rooms, including propulsion, auxiliary machinery, electrical systems, and emergency protocols. By using the simulator, crew members can practice their skills, refine their decision-making processes, and gain confidence in handling complex systems without the risks associated with real-world errors.
The simulator allows trainees to engage in realistic scenarios, such as equipment failures, power management issues, and environmental challenges. This training is invaluable in helping them develop deep technical skills needed to respond effectively under pressure. Given the increasing complexity of ship machinery, which often integrates digital and automated controls, such simulator-based training ensures that personnel are well-prepared for both routine and emergency operations.
Developing Deep Technical Skills with SIRE 2.0 and the GDS Simulator
By integrating SIRE 2.0’s competency standards with the practical capabilities of the GDS Ship Engine Room Simulator, maritime training institutions can foster deep tech skills that are essential in today’s high-stakes maritime environment. Training programs using these tools can address various aspects, including:
Operational Readiness: By simulating real-life engine room conditions, the GDS simulator enables personnel to develop an intuitive understanding of systems and processes, which aligns with SIRE 2.0’s focus on crew readiness and situational awareness.
Crisis Management and Decision-Making: The simulator provides scenarios that replicate emergency situations, allowing trainees to practice crisis response, prioritize actions, and make critical decisions under pressure.
Technical Proficiency: The GDS simulator helps personnel develop advanced skills in troubleshooting and maintaining complex machinery, which is crucial for achieving SIRE 2.0’s standards for operational excellence.
Environmental Compliance: With a growing emphasis on environmental regulations, the simulator enables crew members to familiarize themselves with compliance standards and practice procedures that reduce environmental impact, such as optimizing fuel usage and managing waste effectively.
Safety Protocols: Through realistic training scenarios, the simulator reinforces safety protocols, ensuring that personnel can identify and mitigate risks, which is a core component of the SIRE 2.0 inspection program.
Enhancing the Future of Maritime Training
As the maritime industry continues